Embedding openness into the machine society: OpenMind unifies mind and order
Beyond AI Agents, embodied robots represent another major vertical application scenario in the AI era. Morgan Stanley predicted in a report that the global humanoid robot market could exceed $5 trillion by 2050.
With AI development, robots are gradually evolving from mechanical arms in factories to companions in our daily lives, gaining perception and understanding through AI, even developing independent decision-making capabilities. The challenge is that today’s robots lack standardized communication protocols: each manufacturer uses their own language and logic, with incompatible software and non-shareable intelligence. It’s like owning a car from one manufacturer and a Tesla, but they can’t even assess road conditions together, let alone collaborate on tasks.
OpenMind aims to change this fragmented landscape. They don’t build robots; instead, they’re creating a collaborative system where robots speak the same language, follow the same rules, and complete tasks together. To draw an analogy, iOS and Android enabled the explosion of smartphone applications, Ethereum created a common foundation for the crypto world, and OpenMind wants to build a unified “operating system” and “collaborative network” for robots globally.
In short, OpenMind is building a universal operating system for robots, enabling them not only to perceive and act but also to collaborate safely and at scale in any environment through decentralized coordination.
Who’s Supporting This Open Platform
OpenMind has completed $20 million in seed and Series A funding led by Pantera Capital. More importantly, the “breadth and complementarity” of capital has brought together nearly all the key puzzle pieces in this sector: on one side are long-term forces from Western technology and financial ecosystems—Ribbit, Coinbase Ventures, DCG, Lightspeed Faction, Anagram, Pi Network Ventures, Topology, Primitive Ventures—who understand the paradigm shifts in crypto and AI infrastructure and can provide expertise in models, networks, and compliance for the “agent economy + machine internet”; on the other side is Eastern industrial momentum—represented by Sequoia China’s supply chain and manufacturing systems—which understands what technical and cost thresholds are needed “to turn a prototype into a scalable product.” The combination of these forces gives OpenMind not just funding but also the pathway and resources “from lab to production line, from software to underlying manufacturing.”

This path is also aligning with traditional capital markets. In June 2025, when KraneShares launched its Global Humanoid and Embodied Intelligence Index ETF (KOID), they selected Iris, a humanoid robot jointly customized by OpenMind and RoboStore, to ring the NASDAQ opening bell, becoming the first “robot guest” to complete this ceremony in the exchange’s history. This represents both a synchronization of technology and financial narratives and a public signal about “how machine assets can be priced and settled.”
As Pantera Capital partner Nihal Maunder said:
“If we want intelligent machines to operate in open environments, we need an open intelligence network. What OpenMind is doing for robots is like what Linux did for software and Ethereum for blockchain.”
From Research to Manufacturing
Jan Liphardt, OpenMind’s founder, serves as an Associate Professor at Stanford University and former Berkeley professor with extensive research in data and distributed systems, deeply rooted in both academic and engineering fields. He advocates for open-source reuse, replacing proprietary systems with auditable and traceable mechanisms, and using interdisciplinary approaches to integrate AI, robotics, and cryptography.
OpenMind’s core team comes from institutions like OKX Ventures, Oxford Robotics Institute, Palantir, Databricks, and Perplexity, covering key areas such as robot control, perception and navigation, multimodal and LLM orchestration, distributed systems, and on-chain protocols. Additionally, an advisory team of academic and industry experts (including Stanford robotics lead Steve Cousins, Oxford Blockchain Center’s Bill Roscoe, and Imperial College’s security AI professor Alessio Lomuscio) ensures that robots are “safe, compliant, and reliable.”
OpenMind’s Solution: Two-Layer Architecture, One System of Order
OpenMind has built a reusable infrastructure that allows robots to collaborate and communicate across devices, manufacturers, and even national boundaries:
Device Side: Provides an AI-native operating system, OM1, for physical robots, connecting the entire chain from perception to execution, enabling different types of machines to understand their environment and complete tasks;
Network Side: Builds a decentralized collaboration network, FABRIC, providing identity, task allocation, and communication mechanisms, ensuring robots can recognize each other, assign tasks, and share status when collaborating.
This combination of “operating system + network layer” enables robots not only to act individually but also to collaborate, align processes, and complete complex tasks together in a unified collaborative network.
OM1: AI-Native Operating System for the Physical World
Just as smartphones need iOS or Android to run applications, robots similarly need an operating system to run AI models, process sensor data, make reasoning decisions, and execute actions.
This is where OM1 comes in—an AI-native operating system for real-world robots that enables them to perceive, understand, plan, and complete tasks in various environments. Unlike traditional, closed robot control systems, OM1 is open-source, modular, and hardware-agnostic, capable of running on multiple form factors including humanoid, quadruped, wheeled, and robotic arms.
Four Core Elements: From Perception to Execution
OM1 breaks down robot intelligence into four universal steps: Perception → Memory → Planning → Action. This process is fully modularized by OM1 and connected through a unified data language, enabling composable, replaceable, and verifiable intelligent capabilities.
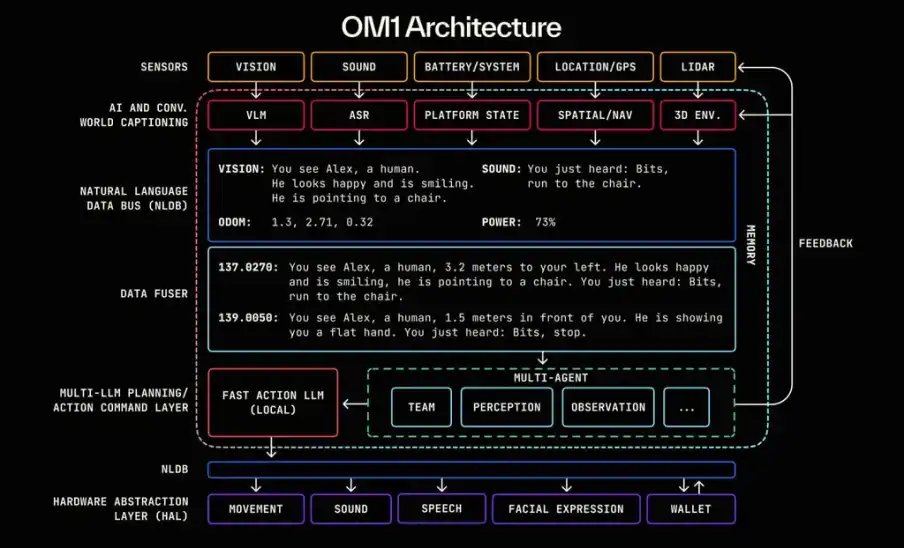
OM1’s architecture
Specifically, OM1’s seven-layer architecture works as follows:
Sensor Layer collects information: cameras, LIDAR, microphones, battery status, GPS, and other multimodal perception inputs.
AI + World Captioning Layer translates information: multimodal models convert visual, audio, and status information into natural language descriptions (e.g., “You see a person waving”).
Natural Language Data Bus (NLDB) transmits information: all perceptions are converted into timestamped language fragments and transmitted between different modules.
Data Fuser combines information: integrates multi-source inputs to generate a complete context (prompt) for decision-making.
Multi-AI Planning/Decision Layer generates decisions: multiple LLMs read the context and generate action plans combined with on-chain rules.
NLDB downstream channel: passes decision results to hardware execution systems through the language intermediate layer.
Hardware Abstraction Layer takes action: converts language instructions into low-level control commands to drive hardware execution (movement, voice broadcast, transactions, etc.).
Quick Start, Widespread Implementation
To quickly transform “an idea” into “a task executable by robots,” OM1 has created an out-of-the-box development pipeline: developers can define goals and constraints using natural language with large models, generating reusable skill packages within hours instead of months of hard coding; multimodal pipelines natively connect LiDAR, vision, and audio, eliminating the need to write complex sensor fusion code; pre-integrated models like GPT-4o, DeepSeek, and mainstream VLMs make voice input and output immediately available; system-level full compatibility with ROS2 and Cyclone DDS, with seamless integration to Unitree G1, Go2, Turtlebot, and various robotic arms through the Hardware Abstraction Layer; native connectivity with FABRIC’s identity, task orchestration, and on-chain settlement interfaces, allowing robots to operate both independently and join a global collaborative network with pay-per-use and audit capabilities.
OM1 has been validated in multiple real-world scenarios: the quadruped platform Frenchie (Unitree Go2) successfully completed complex field tasks at the 2024 USS Hornet Defense Technology Exhibition, while the humanoid platform Iris (Unitree G1) conducted on-site human-machine interaction at Coinbase’s booth at EthDenver 2025, and entered American university courses through RoboStore’s education project (one of Unitree’s largest distributors in the US), extending the same development paradigm to frontline teaching and research.
FABRIC: Decentralized Human-Machine Collaboration Network
Even with strong standalone intelligence, if robots cannot collaborate on a trustworthy basis, they remain isolated. Real-world fragmentation stems from three fundamental problems: identity and location cannot be standardized and proven, making it difficult for external parties to trust “who I am, where I am, what I’m doing”; skills and data lack controllable authorization paths for secure sharing and invocation across multiple entities; control rights and responsibility boundaries are unclear, with operational parameters, authorization scope, and verification mechanisms difficult to pre-agree or trace afterward. FABRIC addresses these pain points with a system-level solution: using decentralized protocols to establish verifiable on-chain identities for robots and operators, providing integrated infrastructure for task publishing and matching, end-to-end encrypted communication, execution records, and automatic settlement around these identities, transforming collaboration from “temporary connections” to “documented institutions.”
Operationally, FABRIC functions as a network layer that combines “positioning, connection, and scheduling”: identity and location are continuously signed and verified, giving nodes naturally “visible and trustworthy” peer relationships; point-to-point channels act like on-demand encrypted tunnels, enabling remote control and monitoring without public IP addresses or complex network settings; the entire process from task publication to acceptance, execution to verification is standardized and recorded, enabling both automatic profit distribution and deposit refunds during settlement, as well as verification of “who completed what, when and where” in compliance or insurance scenarios. On top of this, typical applications naturally emerge: enterprises can remotely maintain equipment across regions, cities can turn cleaning, inspection, and delivery into scalable Robot-as-a-Service, vehicle fleets can report road conditions and obstacles in real-time to generate shared maps, and when needed, nearby robots can be dispatched for 3D scanning, building surveying, or insurance evidence collection.
As identity, tasks, and settlement are managed by the same network, collaboration boundaries are clearly defined in advance, execution facts are verified afterward, and skill invocation has measurable costs and benefits. In the long term, FABRIC will evolve into an “application distribution layer” for machine intelligence: skills circulate globally with programmable authorization terms, and data generated from invocations feeds back into models and strategies, enabling the entire collaborative network to continuously self-upgrade within trustworthy constraints.
Web3 Is Writing “Openness” Into Machine Society
The robotics industry is rapidly consolidating around a few platforms, with hardware, algorithms, and networks locked in closed stacks. The value of decentralization lies in enabling robots of any brand and region to collaborate, exchange skills, and complete settlements on the same open network without relying on a single platform. OpenMind encodes this order through on-chain infrastructure: each robot and operator has a unique on-chain identity (ERC-7777, an identity standard) with verifiable hardware fingerprints and permissions; tasks are published, bid on, and matched under public rules, generating on-chain encrypted proofs with time and location during execution; contracts automatically settle profits, insurance, and deposits after task completion, with results verifiable in real-time; new skills set invocation counts and compatible devices through contracts, enabling global circulation while protecting intellectual property. Thus, the robot economy inherently possesses anti-monopoly, composable, and auditable genes from birth, with “openness” written into the underlying protocols of machine society.
Helping Embodied Intelligence Break Out of Isolation
Robots are moving from exhibition stages to everyday settings: monitoring hospital wards, learning new skills on campuses, conducting inspections and modeling in cities. The real challenge isn’t stronger motors but enabling machines from different sources to trust each other, exchange information, and work together; beyond technology, distribution and supply are even more critical for scaling.
OpenMind’s implementation path therefore starts with channels rather than parameter stacking. Partnering with RoboStore (one of Unitree’s largest distributors in the US), they’ve turned OM1 into standardized curriculum and experimental kits, advancing integrated hardware and software supply simultaneously across thousands of American universities. The education system represents the most stable demand side, directly embedding OM1 into the developer and application pipeline for the coming years.
For broader social distribution, OpenMind leverages its investor ecosystem to create platform-based “software export channels.” Extensive crypto ecosystems like Pi enhance the potential of this model, gradually forming a positive flywheel creating an ecosystem of developers, users, and paying customers. With education channels providing stable supply and platform distribution bringing scale demand, OM1 and upper-layer applications gain a replicable expansion trajectory.
In the Web2 era, robots were often locked in single-vendor closed stacks, with functions and data unable to flow across platforms; after connecting curriculum standards with distribution platforms, OpenMind makes openness the default setting: the same system enters campuses, moves toward industries, and continuously spreads through platform networks, making openness the default starting point for scaled implementation.
Disclaimer:
- This article is republished from BlockBeats, and the copyright belongs to the original author BlockBeats. If you have objections to the republication, please contact the Gate Learn team, who will handle it according to the relevant procedures as quickly as possible.
- Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article represent only the author’s personal views and do not constitute any investment advice.
- Translations of the article in other languages are provided by the Gate Learn team and may not be copied, distributed, or plagiarized without mentioning Gate.
Related Articles

Arweave: Capturing Market Opportunity with AO Computer

The Upcoming AO Token: Potentially the Ultimate Solution for On-Chain AI Agents

Dimo: Decentralized Revolution of Vehicle Data

AI Agents in DeFi: Redefining Crypto as We Know It

Mind Network: Fully Homomorphic Encryption and Restaking Bring AI Project Security Within Reach
